
#METAL ION REACTIVITY SERIES SERIES#
Only a metal higher in the reactivity series will displace another. Therefore the elemental metal will 'displace' the ionic metal over time, thus the two swap places. When a metal in elemental form is placed in a solution of a metal salt it may be, overall, more energetically feasible for this "elemental metal" to exist as an ion and the "ionic metal" to exist as the element. However it is defined by the nature of the metals in single displacement reactions. The reactivity series determines qualitatively characteristics such as the reactions with water, air and acids as demonstrated above.

This is markedly different from the table below. The reactivity series taught in the US is defined by the ease of oxidation and corresponds to the ordering of the table of standard electrode potentials. A few drops of universal indicator have been added to the water.In the UK a reduced version of the series below is taught as part of the GCSE chemistry course, leading to various mnemonics being invented to aid memory. Questionĭescribe and explain the observations when a small piece of lithium is placed on the surface of a big container of water. In general, the more reactive the metal, the more rapid the reaction is.

Sodium + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen For example, sodium reacts rapidly with cold water: When a metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and hydrogen are formed.

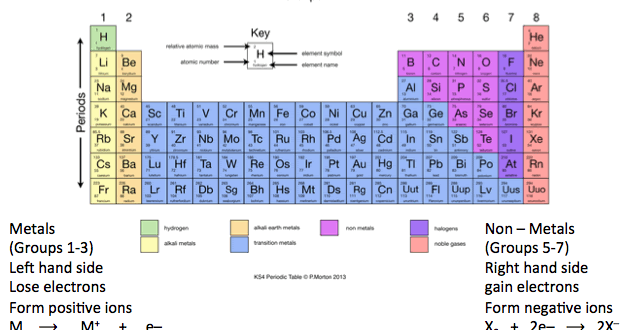
Hydrogen and carbon are shown for comparison. The table summarises some reactions of metals in the reactivity series. the more easily it loses electrons in reactions to form positive ions (cations).In general, the more reactive a metal is: The reactivity series of metals is a chart showing metals in order of decreasing reactivity. When metals react with other substances, the metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
